Fuse
The fuse is a protective device that interrupts a circuit when a specific electric current is applied for a defined period of time. Examples include the melting fuse and the miniature circuit breaker. See Fig. 1 Fuse
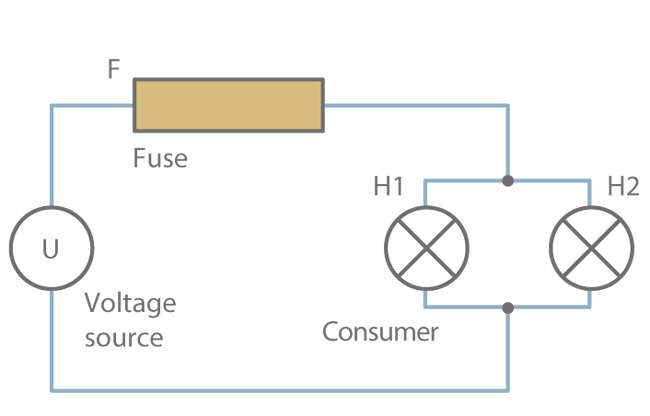
Fig. 1 Fuse: Circuit with fuse protection
When a melting fuse is triggered, the circuit is interrupted by the thermal effect of the current, which also destroys the fuse. This fuse can then no longer be used.
A standard variant is the device and micro fuse, which is also referred to as the G-fuse or glass tube fuse and comprises a small glass or ceramic tube with a metal cap on both ends. A fuse element is integrated in the tube.
Key values such as the nominal current, maximum voltage, and tripping characteristic of the G-fuse are indicated on the metal caps. The tripping characteristic indicates how quickly the fuse responds to overcurrent, whereby a distinction is made between FF (fast fuse) (< 20 ms), F, M, T, and TT (super time lag) (> 300 ms).
