Peripheral pump
Peripheral pumps, also referred to as regenerative pumps (also see Side channel pumps), are centrifugal pumps whose impeller (see Peripheral impeller) rotates in a largely concentric casing channel with an inlet and an outlet opening. As the fluid handled repeatedly circulates between the impeller and the casing channel the energy transferred to it is very high.
In total the fluid moves along the circumference from the inlet to the outlet of the casing with increasing pressure. A stripper arranged between the outlet and the inlet prevents a hydraulic short circuit between the high-pressure and the low-pressure side of the casing channel.
Due to the large increase in energy, peripheral pumps can be relatively small in size. They are often designed as close-coupled pumps.
See Figs. 1, 2 Peripheral pump
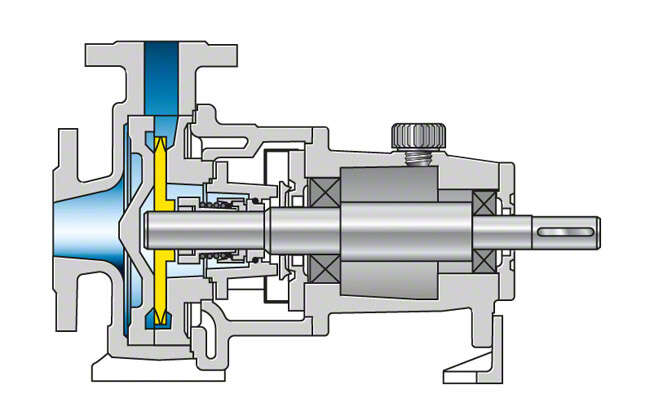
Fig. 1 Peripheral pump: Single-stage pump
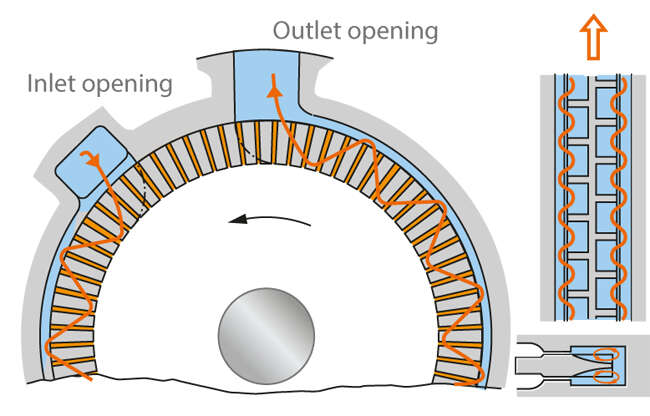
Fig. 2 Peripheral pump: Energy supply principle in a peripheral pump impeller
The head coefficients, or pressure coefficients, of peripheral pumps exceed those of side channel pumps and their characteristic curves are steeper. The pump input power of peripheral pumps decreases with increasing flow rate.
Peripheral pumps with several (up to three) blade wheels arranged at the various diameter levels of the impeller are considered multistage pumps. At common speeds of 2,900 rpm they produce heads of up to 1,200 m. For low flow rates peripheral pumps can partly be used for the same applications as high-pressure geared pumps (see Geared pump) and even positive displacement pumps. See Fig. 3 Peripheral pump
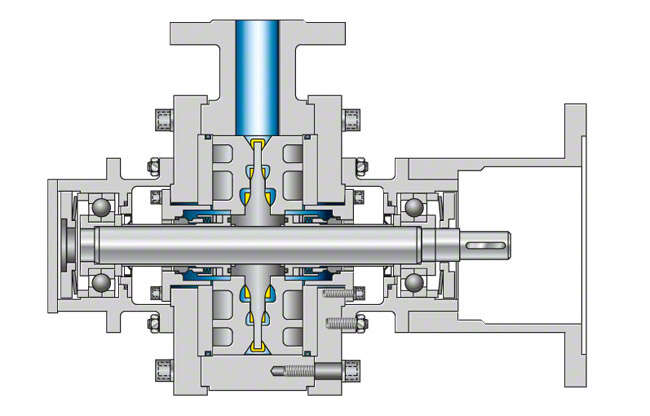
Fig. 3 Peripheral pump: Multistage pump
Another characteristic of peripheral pumps is that, unlike other centrifugal pumps, they can transport fluids with a relatively high gas content (see Two-phase flow). Even severe vapour bubble formation (see Cavitation) will not lead to flow cut-off or have a major impact on the pump's smooth running. The H/Q curve will deviate gradually rather than suddenly from the H/Q curve measured in cavitation-free conditions. Another advantage is the symmetrical approach flow (see Double-suction pump) to the impeller (low axial thrust). See Fig. 4 Peripheral pump
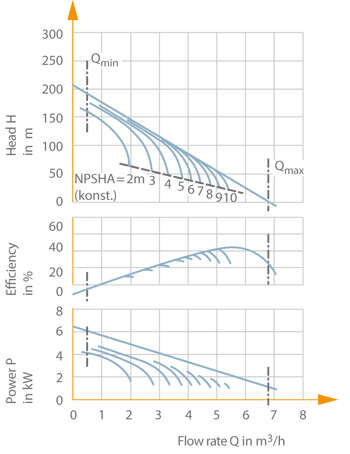
Fig. 4 Peripheral pump: Characteristic curves of a peripheral pump (nom. diameter DN 25, impeller diameter 125 mm, speed n = 2900 rpm)
The efficiencies of peripheral pumps are lower than those of radial pumps. They are suitable for pumping uncontaminated liquids, e.g. as boiler feed pumps for small boilers, as pressure boosting pumps, car wash pumps, as pumps for the chemical industry and for all applications in which low flow rates have to be pumped at high pressure.
