Terminal gland
The terminal gland facilitates the supply of current through the motor housing to the winding. Submersible windings use a pressure-sealed terminal gland in the form of a copper connection bolt as is used fo wet rotor motors, e.g. in glandless pumps for. The bolt is insulated at the housing wall by insulating sleeves, sealed by an O-ring, and pressure-sealed by a threaded bushing. See Fig. 1 Terminal gland
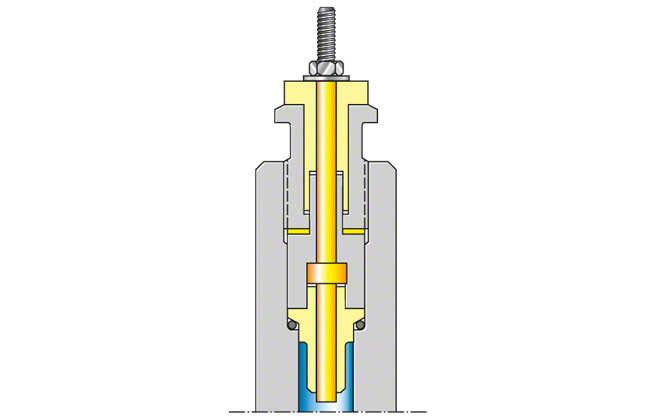
Fig. 1 Terminal gland: Example for glandless pumps with wet winding (wet rotor motor)
